Smart factories are currently transforming the manufacturing industry significantly. They are changing not only the manufacturing process but also the way businesses operate and how consumers interact with products.
 A smart factory is a manufacturing facility that uses cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data to automate production processes, increase efficiency, and improve product quality. These factories can gather and analyze real-time data from machines, sensors, and other connected devices, enabling optimization of production processes, identification of potential issues, and proactive decision-making.
A smart factory is a manufacturing facility that uses cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and big data to automate production processes, increase efficiency, and improve product quality. These factories can gather and analyze real-time data from machines, sensors, and other connected devices, enabling optimization of production processes, identification of potential issues, and proactive decision-making.
Adopting smart factory technologies offers numerous substantial advantages. McKinsey & Company conducted a study showing that productivity can increase by 25-30% with smart factories. The study also revealed potential cost reductions of up to 20% and product quality improvements of up to 15%. These improvements primarily stem from automating previously manual tasks.
Implementing smart factory technologies ensures consistent and high-quality product output through real-time monitoring and early detection of deviations or anomalies. Manual labor can be eliminated, leading to cost reduction and optimized energy and material usage. Additionally, smart factories provide enhanced flexibility, enabling swift adaptation to changes in demand or supply, thereby improving responsiveness to market dynamics. Lastly, smart factories enhance customer service by providing real-time updates and information on order statuses, minimizing customer wait times and enhancing overall satisfaction.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge the challenges associated with smart factories. Initially, the implementation costs of smart factory technologies can be considerable due to the need for new equipment, employee training, and customized software development. Additionally, there is a shortage of skilled workers proficient in operating and maintaining smart factory technologies, which is expected to persist and pose a significant challenge to widespread adoption. Furthermore, the connectivity of smart factories to the internet exposes them to potential cybersecurity threats, necessitating robust security measures to protect sensitive data and prevent cyberattacks.
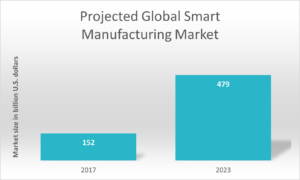
The future of smart factories looks promising, with the adoption of these technologies projected to continue growing. Manufacturers are increasingly attracted to the extensive benefits they offer in terms of productivity, quality, and profitability. As smart factory technologies evolve further, they are expected to become even more sophisticated and powerful, unlocking greater opportunities for improvement. Smart factories are poised to revolutionize the manufacturing industry and reshape its landscape in the years to come.


